- The marijuana plant produces more than 500 compounds, and around 113 of them are cannabinoids.
- Cannabinoids are hard to identify as they appear in very low concentrations. This makes it difficult to determine the exact number that are produced by the plant.
- However, around 10 of them appear in significant quantities.
- Here we will describe marijuana’s main cannabinoids and their properties.

What are phytocannabinoids?
As we explained in this post, there are several types of cannabinoids: human cannabinoids (or endocannabinoids), marijuana cannabinoids, and synthetic cannabinoids (which are designed in labs.) Here we will focus on phytocannabinoids, which are the cannabinoids produced by the marijuana plant.
Phytocannabinoids are chemical compounds found in the bud trichomes of the cannabis plant. They are characterised by a 21 carbon structure, normally consisting of three rings: benzene, cyclohexene, and tetrahydropyran. These active compounds are secondary metabolites, that is, they do not aid in the growth and development of plants but act as an immune system that protects plants from parasites, plagues, and predators.
The cannabis plant produces hundreds of compounds that perform different functions. Terpenes, for instance, are the molecules that give that characteristic aroma to cannabis. Chlorophyll is responsible for the colour of the leaves, and cannabinoids produce the psychoactive effect connected to cannabis.
But not all cannabinoids have psychoactive properties, and they can have other functions too. You have probably heard of THC and CBD, marijuana's two main and most researched cannabinoids. Most cannabinoids do not cause the well-known euphoria related to cannabis use, but can activate several processes in the human body that can have diverse effects. In fact, the list of euphoria-inducing cannabinoids is short, with THC right at the top. THCV is also psychoactive but its effect is not as long-lasting as THC's.
So what happens with the rest of cannabinoids? As explained below, these other cannabinoids have many applications, both therapeutic and recreational. For instance, their presence and concentration in the different marijuana strains have an influence on THC's intoxicating effect.
A clear example of this is CBD's modulating effect. This is why CBD-rich strains cause a longer-lasting euphoria feeling. Therefore, knowing exactly what we are consuming is paramount. It is essential to obtain information about the specific strain that we are going to grow or buy, so that we know how it is going to affect our body, be it for therapeutic or recreational purposes.
Cannabinoids in their acidic form
The cannabis plant produces cannabinoids in their acidic or non-psychoactive form. This means that, when cannabinoids are present in the resin of fresh buds, either freshly cut or still in the plant, they do not produce the same effects as after decarboxylation, which occurs with heat or oxidation.
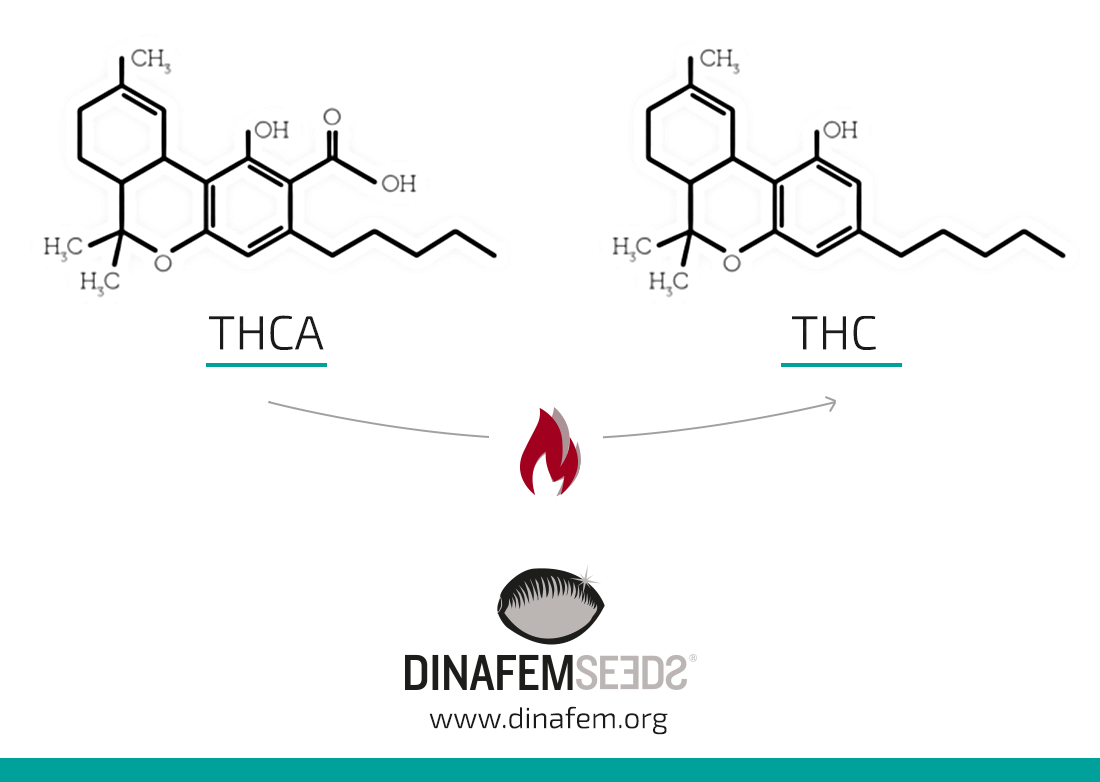
This means that the renowned THC is not present in the cannabis plant. What we find is THCA, a compound which does not give you the 'high' normally associated with cannabis use. When heat is applied, for example when we smoke weed, it is then that acidic cannabinoids transform into their neutral counterparts.
The main acidic cannabinoids found in marijuana are the following:
- CBGA
- THCA
- CBDA
- CBCA
- CBGVA
- THCVA
- CBDVA
- CBCVA
These acidic cannabinoids become active through the decarboxylation process. What we normally ingest are cannabinoids in their neutral form, unless we are drinking a cannabis juice made with freshly-cut buds.
Cannabinoids in their neutral form
The following are the main neutral cannabinoids found in marijuana:
THC or tetrahydrocannabinol
THC is the best known cannabinoid and is responsible for the plant's psychoactive effect. Raphael Mechoulam was the first to isolate and synthesize THC in 1964. His discovery led the way to research on other cannabinoids and the endocannabinoid system. Like CBD, THC appears in cannabis in greater quantities than other cannabinoids. When THC interacts with the receptors in the brain and the nervous system, a chemical reaction occurs, which is what produces the well-known cannabis 'high'.

What are the effects of THC on the human body?
Depending on the dosage, THC can cause:
- Short-term memory impairment
- Euphoria
- Relaxation
- Pain relief
- Hunger
- Sleepiness
- Anxiety
- Dry mouth
- Red eyes
Even though THC has become famous for its role in the recreational use of cannabis, it also showcases many medicinal properties. It has been proved that this cannabinoid can be effective in the treatment of several diseases, such as chronic neuropathic pain, insomnia, glaucoma, sleep apnoea, fibromyalgia, etc.
CBD or cannabidiol
CBD is the second most abundant cannabinoid in marijuana, and has revolutionised the cannabis industry in the last few years. It does not cause any psychoactive effects and is related to cannabis therapeutic applications, though it can also be useful recreationally. By means of its interaction with the endocannabinoid system receptors, CBD can help keep an equilibrium between several body functions, especially within the immune system. CBD also helps reduce some of the less pleasant effects of THC, like anxiety or mouth dryness.
CBN or cannabinol
CBN does not produce any psychoactive effects, but it stands out for its potent sedative properties. To give you a comparison, 5 mg of CBN is equivalent to 10 mg of Diazepam. As it does not cause THC's intoxicating effect, CBN can help you sleep without giving you a 'hangover' the following day. In a few words, it is sleep-inducing without losing mental clarity. Some drugs for the treatment of insomnia can cause addiction; on the contrary, CBN is a natural alternative with a very low addiction risk. Higher levels of CBN can be found in late harvests. This happens because, once 'optimum harvest time' has been reached, THC turns into CBN. Therefore, if what you want is cannabis with a more powerful narcotic effect, you can cut your plants one or two weeks past that point.
CBC or cannabichromene
CBC is considered one of 'the main six cannabinoids' found in marijuana. Although it has no psychoactive properties like THC's, several studies have confirmed that CBC has great medicinal potential. And though CBC was discovered 50 years ago, it seems that research has only been concentrating on its therapeutic potential over the last few years. CBC does not connect to CB1 receptors in the endocannabinoid system but connects to TRPV1 and TRPA1 receptors. These belong to the transient receptor potential family, located in the nervous system, and are associated with pain perception, which has prompted scientists to believe that CBC could have an important role in the near future as an analgesic.
CBG or cannabigerol
Although CBG's levels are normally low (approximately 1%), it is important to keep in mind that this chemical compound is the predecessor of THCA, CBDA, and CBCA. Due to its outstanding therapeutic properties, some breeders have been trying to create new CBG-high strains over the last few years, with the first ones already appearing on the market.
THCV or tetrahydrocannabivarin
THCV's molecular structure is very similar to tetrahydrocannabinol's. It appears in higher concentrations in Afghan varieties and is also psychoactive, but the effect wears off around 20-25% more quickly than in THC.
CBDV or cannabidivarin
CBDV has a similar molecular structure to CBD's. It is non-psychoactive and is found in higher concentrations in Indica landrace strains, especially the ones with low THC and high CBD levels, that are grown near the mountainous areas of North India and used to make the world-famous Nepalese hash.







Comments from our readers
There are no comments yet. Would you like to be the first?
Leave a comment!Did you like this post?
Your opinion about our seeds is very important to us and can help other users a lot (your email address won't be made public).