- As part of the series of articles "This is what we do in the Dinafem Seeds laboratory ", today’s post will look at the Dinalab’s analysis process for cannabinoids and terpenes.
- The focus of the scientific work carried out by Dinafem’s technicians is on the active compounds found in the plants we use for breeding, as well as in the genetics of the seeds we sell. In previous articles, we discussed the importance of obtaining reliable data on these compounds, and now we’ll get a deeper understanding of how these data are obtained.
- What goes on inside gas and liquid chromatographs? How do these devices provide data that can help the decision-making process of creating new strains? How do our lab technicians use the cannabis samples in order to ensure accurate results?
- Oier and Pierre Antoine, the Dinafem Seeds laboratory technicians, have the answers.

What cannabinoids – the active ingredients in cannabis that interact with the human endocannabinoid system – does a particular cannabis strain contain? In which concentration? What are its most pronounced aromas and what amounts of the terpenes that cause them does it contain? These are just some of the questions regarding the distinctive features of cannabis strains that cannot be answered using the senses. In fact, the use of specific equipment which has been properly calibrated by qualified staff in order to obtain relevant data from the cannabis plants is the only way to get an accurate idea of what individual cannabis strains are composed of – as well as to understand how to interpret this information.
Cannabis plants contain some 500 active compounds, among which at least 113 are cannabinoids. Work in the Dinafem Seeds laboratory focuses on identifying which of these compounds – and in which concentration – is found in each strain. Something similar is done for terpenes – the substances that give cannabis different scents – which are analysed for types and concentrations. Out of cannabis' 500 compounds, the Dinalab technicians work with about 10 cannabinoids and 40 terpenes – the most relevant in terms of amounts and importance. Knowing the concentration of both cannabinoids and terpenes is a top priority in the laboratory since it is these compounds that shape the effect of cannabis by interacting with the body's endocannabinoid system. At this point it is worth recalling that cannabinoids are not the only substances influencing cannabis' effect, which can also be modulated by the action of terpenes. This is the reason why two strains with the same cannabinoid profile but different terpene concentrations can produce two entirely different effects.
Once Oier and Pierre Antoine, the Dinafem Seed technicians, have collected representative samples from the grows, they process them and use them to analyse the different cannabis strains. Here's how.
Calibration of the chromatographs
The first step to analysing cannabinoids and terpenes is calibrating the machines involved in the process. This is done by telling the chromatographs what one milligram of substances like THC and CBD is so that they can measure their concentrations using the introduced standards or calibration points. Our laboratory technicians introduce these data using extracts based on standards defined by chemical companies. This means working with precisely-weighed, purified cannabinoids which allow highly accurate results. Once the extracts are ready, Oier and Pierre Antoine prepare various dilutions for each compound so that the whole spectrum is covered inside the chromatographs.
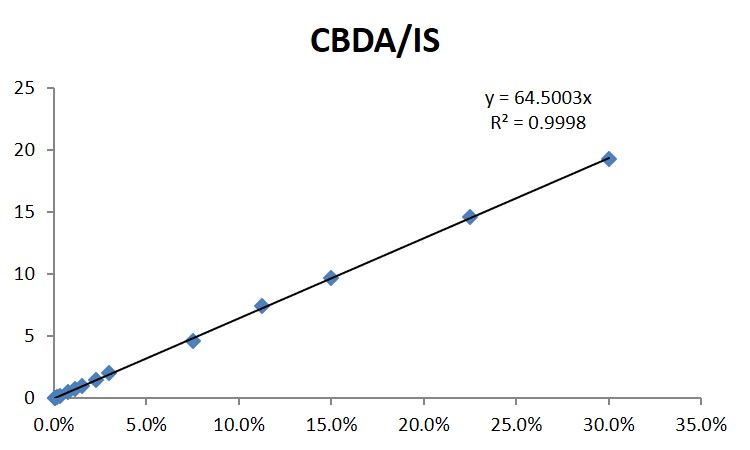
In addition to calibration points, the technicians define quality control parameters. These are different concentrations of the base standard that are introduced in the chromatograph whenever an unknown substance is analysed in order to ensure the calibration is correct.
Analysis of cannabinoids by liquid chromatography
At Dinafem Seeds, cannabinoids are analysed by liquid chromatography. As explained in previous articles, cannabinoids can be either acids or bases depending on the temperature they're exposed to, which has the ability to change their molecular structure. Basic cannabinoids include THC, CBD and CBN, which are expressed as THCA, CBDA and CBNA in the acid form. Basic cannabinoids are simply decarboxylated acid cannabinoids. This is why cannabinoids are found in acid form in fresh cannabis plants but are transformed into bases when the buds undergo combustion as a result of smoking.
In the Dinalab, only acid cannabinoids are considered for analysis. "Analysing acids is the only way to know what's really inside a plant," says lab tech Oier. "The acid/base conversion rate is not one hundred percent accurate, so working with basic cannabinoids wouldn't be as effective. Also, it would allow us to know what cannabinoids a smoker would get but not the cannabinoid content of a cream made from plant matter that has not been decarboxylated," he adds.



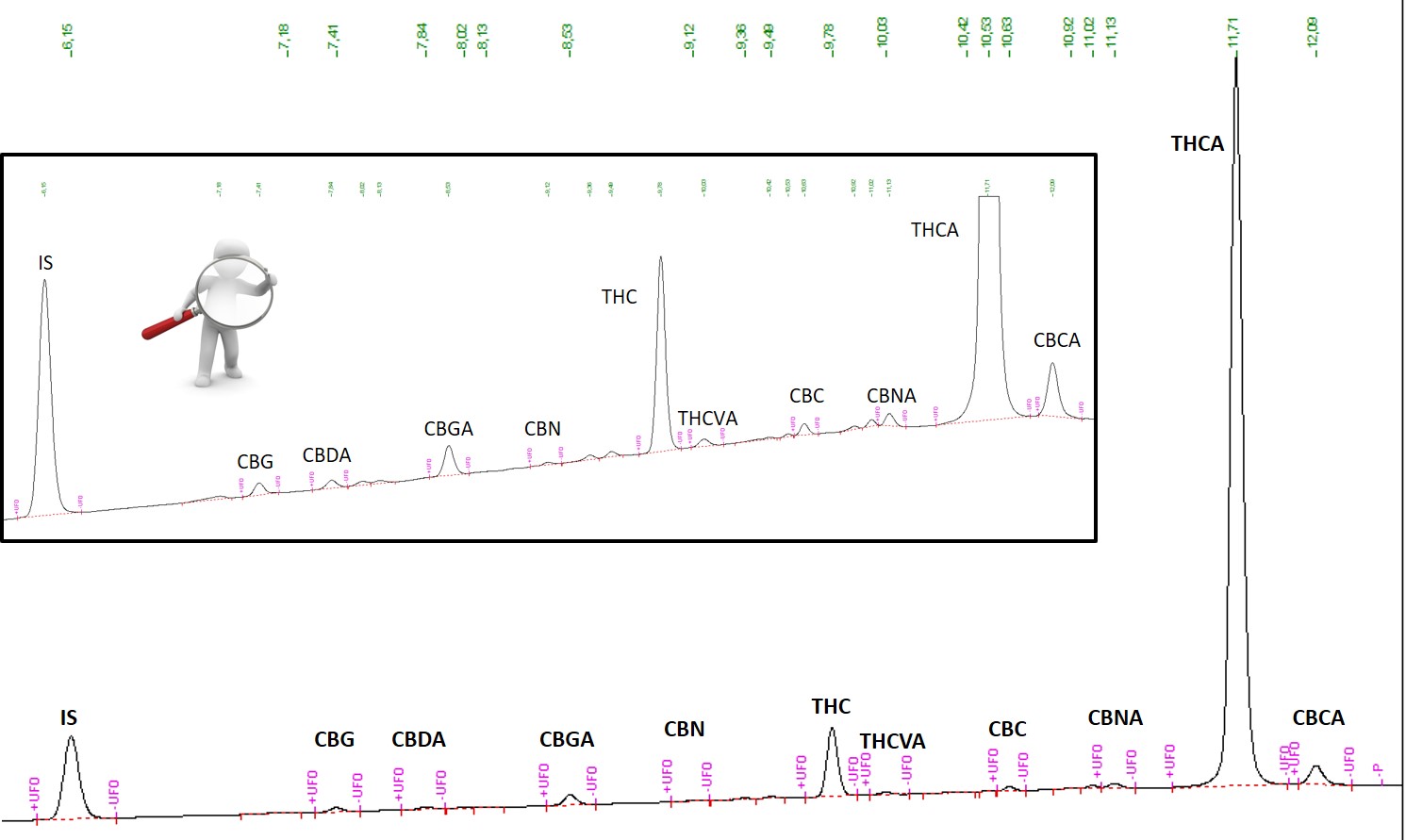
Once in the liquid chromatograph, the ethanol-diluted cannabis samples undergo two processes. The first involves separating the compounds in the vials, which occurs inside a 150-cm column where the liquids are subjected to pressure. Next is to identify the separated compounds. Because the elements to detect have been introduced in the chromatograph during the calibration stage, this can be done by going through the different compounds with a light source, which will produce different peaks for different cannabinoid concentrations depending on the amount of light absorbed.
At the end of the process, this information is translated into a graph like this.
Analysis of terpenes by gas chromatography

Terpenes are the compounds responsible for cannabis' aroma. Cannabis strains contain many different types of them, showing varying organoleptic traits and effects depending on which terpenes are more abundant. Because they're volatile substances, the Dinafem Seeds laboratory technicians prefer to analyse them by gas chromatography. "It makes more sense to analyse volatile compounds with a gas," they say.
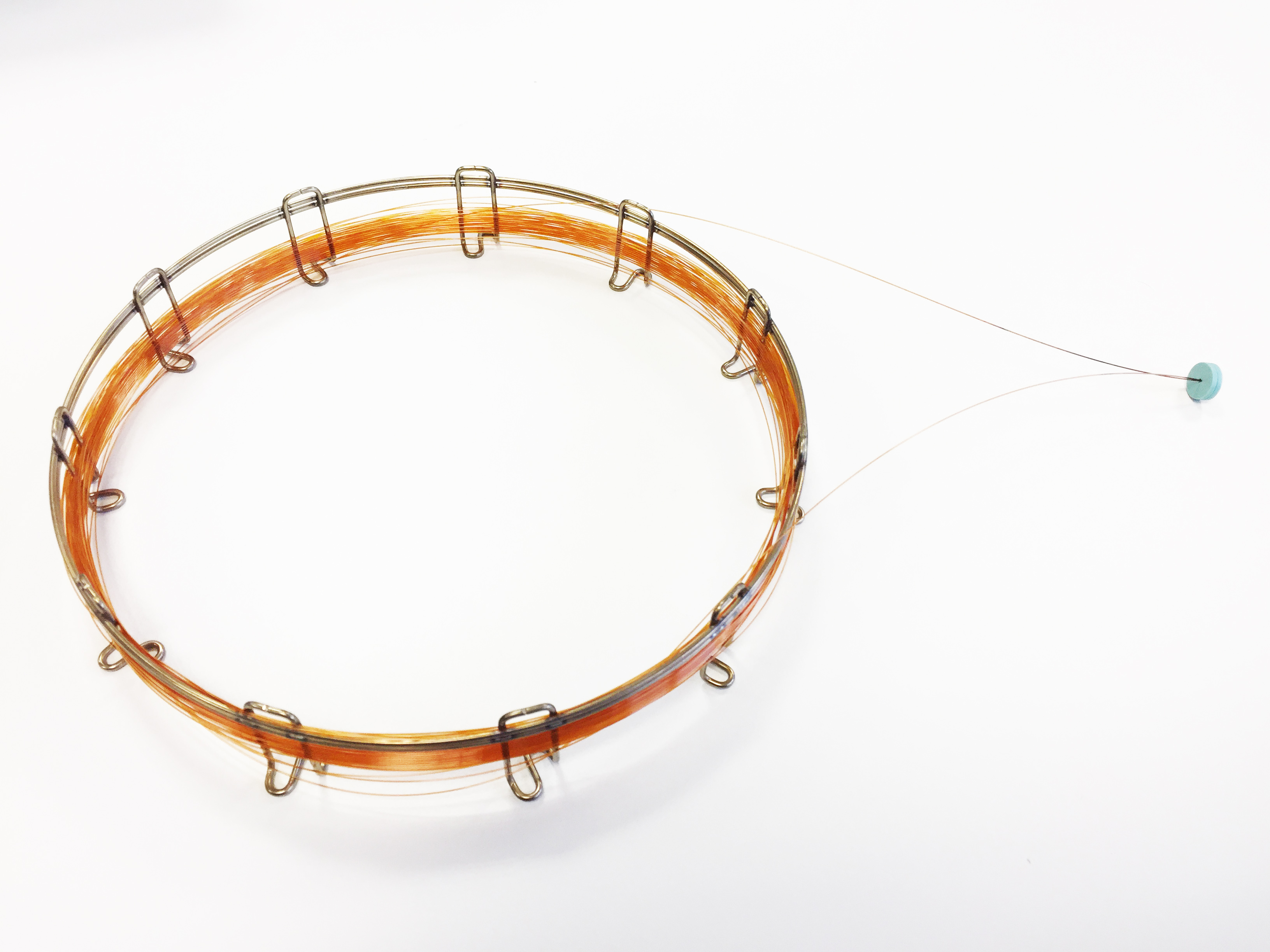
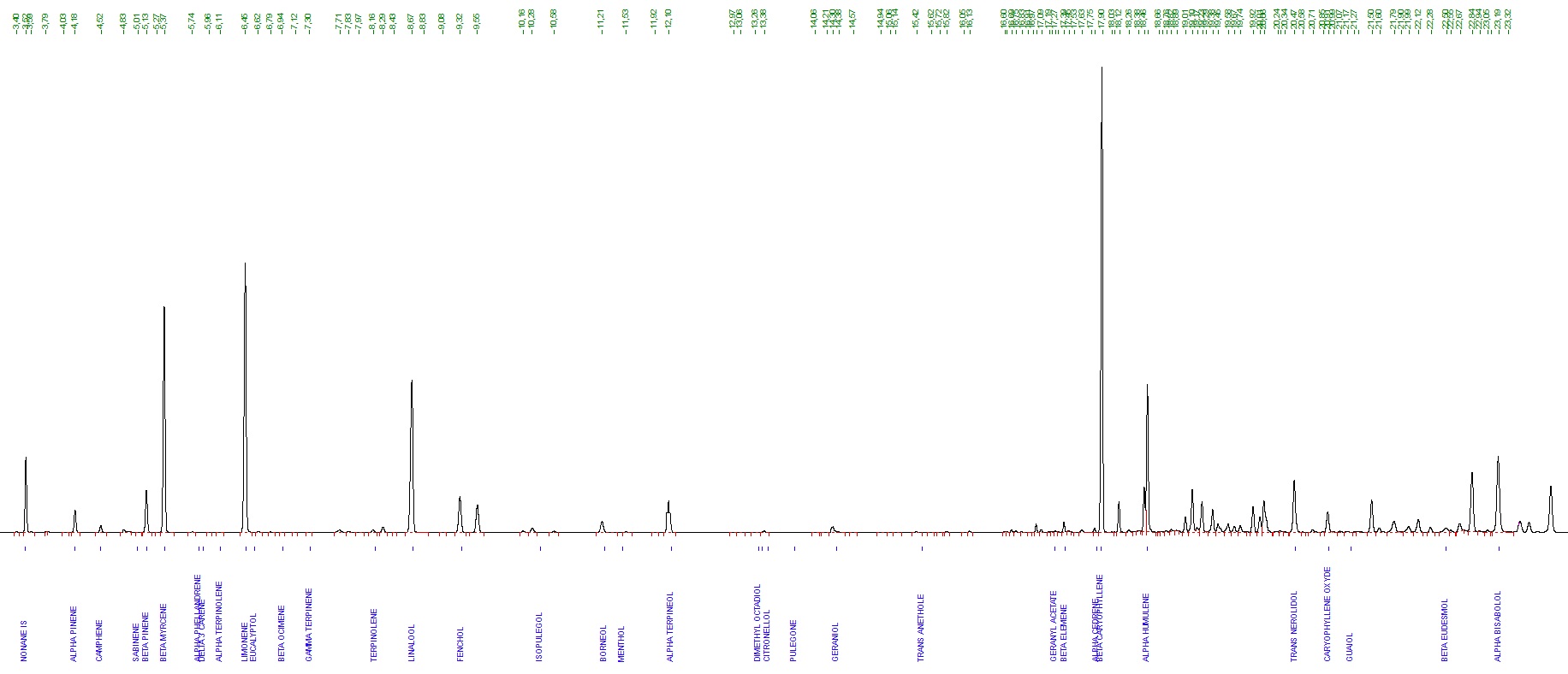
Gas chromatography uses a 30-metre coil column that interacts with the terpenes. When the samples are introduced in the chromatograph, these are propelled by a gas along the column, which is housed in an oven where temperature rises gradually starting at 60 ºC. As the terpenes reach their boiling point, they travel through the coil at different speeds depending on their composition, where they are separated based on their traits and column affinity.
Once the "trip" is over, the chromatograph produces a graph like the one below, indicating which of the terpenes contemplated during the calibration stage are contained in the samples and in which amounts.
Sources:
This article has been written with the help of the Dinafem Seeds laboratory technicians, Oier Aizpurua and Pierre Antoine Aulas, who kindly answered all our questions and showed us how they work in the Dinalab.
Oier Aizpurua holds a BSc in Chemistry, an MSc in Toxicology and a PhD in Analytical Chemistry from the University of the Basque Country. He specialises in cannabinoid and terpene extraction and analysis, as well as in the analysis of cannabinoid metabolites in biological samples.
Pierre Antoine Aulas holds a BSc in Pharmaceutical Sciences form the University of Lille, completed studies on Plant Sciences in Manipal, India, and has an MSc in Neuropharmacology, focusing on CBD formulations as a treatment for children suffering from epilepsy in Israel.





Comments from our readers
There are no comments yet. Would you like to be the first?
Leave a comment!Did you like this post?
Your opinion about our seeds is very important to us and can help other users a lot (your email address won't be made public).