- During the weekend that we spent in Peterborough at the Product Earth Expo fair, we had the pleasure to meet and interview Viola Brugnatelli, a neuroscientist dedicated to the research of cannabinoids, their properties and their possible medical applications in treating neurodegenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
- Besides, we talked about a delicious way to reap all the benefits that cannabis can offer to our health: fresh cannabis juice.

In order to disseminate the results of her scientific research and those of other professionals, Viola created Nature Going Smart, a blog that provides authoritative information on cannabinoids and their therapeutic use. There is much scientific evidence supporting the benefits of cannabinoids to our body; however, the way we consume them has great influence on the properties of cannabis compounds.
Cannabis fresh juice of is an excellent way to get all the health benefits marijuana can offer while avoiding the psychoactive effect of THC. Yes, you read that right! How? Consuming fresh marijuana does not produce the typical cannabis buzz to which we are accustomed. Want to know why? Keep reading…
Why is cannabis fresh juice so beneficial?
The marijuana plant produces 421 chemicals, 80 of which are cannabinoids. Among them is the D9-THCA, which is the acid form of the famous D9-THC, the main responsible for the effect we all know as cannabis "high". When we consume raw cannabis (without applying heat or let it dry) i.e. the fresh flower obtained directly from the plant, we don't feel any effect because the D9-THCA, which does not produce any psychoactive effect, has not had time to become D9- THC. For this to happen, cannabis must go through a decarboxylation process, which occurs, for example, when it is heated, through vaporization or combustion.
What are the benefits of fresh cannabis juice?
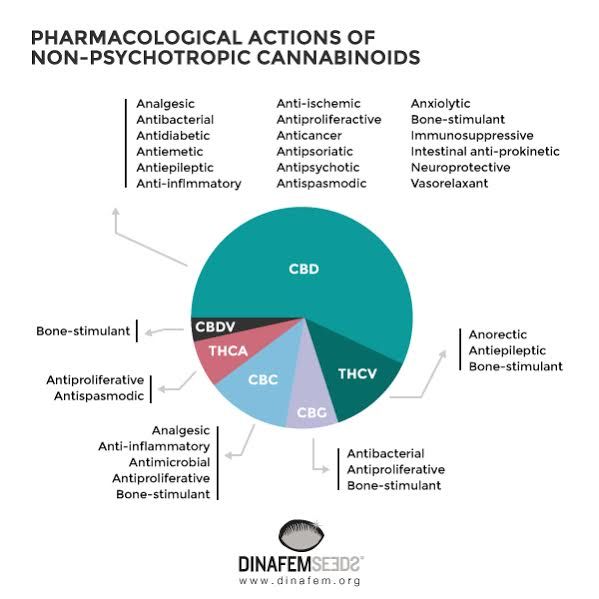
- Analgesic and anti-inflammatory: THCA and CBD have proven to be powerful allies to combat chronic pain, even for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. THCA is a powerful anti-inflammatory due to its ability to inhibit cyclooxygenase1and 2. Ref. (2, 3, 4)
- Antibacterial: cannabinoid acids D9-THC, CBD, CBN, the CBC and CBG have an important anti-fungal and antibiotic capacity. (1)
- Anti-emetic: Both D9-THCA, D9-THC and CBD have proven to be great allies to alleviate nausea. (5)
- Antiepileptic: the findings in the medical and scientific fields on the effectiveness of CBD against refractory epilepsy cases (especially in children with Dravet syndrome) have reopened the eternal debate on the legalization of medical cannabis. In addition to CBD, there are other components in cannabis, such as CBC, which decrease the duration of seizures. (6, 1)
- Antipsychotic: Some studies suggest that CBD counteracts the psychotic effects produced by THC. This substance acts in a very similar way than atypical antipsychotics such as clozapine, without the side effects of typical anti-psychotics. (7)
- Anxiolytic: several studies have shown that CBD acts as a powerful anxiolytic but without the adverse effects of benzodiazepines. CBD or cannabidiol attenuates the response of the body to stress. This is why this cannabis compound is a powerful ally against insomnia and post-traumatic stress. (8)
- Bone formation: scientific studies show that the CBDV, D9-THCV and CBD cannabinoids contribute to bone formation and regeneration from the recruitment of stem cells in the bone marrow. (9)
- Cerebral ischemia and infarction: the CBD and the D9-THC can help reverse the negative consequences of a cerebral ischemic attack in the brain. (10)
- Chronic Fatigue: Cannabis fresh juice provides many nutrients to the body such as edestin and essential amino acids, which help increase energy. (11)
- Neuroprotective: Numerous scientific studies have concluded that CBD is a powerful neuroprotective, very effective for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's or Huntington's disease. (12)
How to prepare fresh cannabis juice at home?
Making your own fresh cannabis juice at home is very simple; you only need a marijuana plant in flowering stage, preferably in its eighth week, as this is when the flower contains the greater concentration of cannabinoids and terpenes. It is very important to use freshly-cut buds to make the juice. In order to increase its therapeutic benefits, we recommend making it with buds of a strain rich in CBD. Autoflowering strains with a high CBD content like Haze auto CBD are perfect for this purpose, as they are discreet and have a very short life cycle and can be grown in the balcony of your home.
Steps to prepare the fresh cannabis juice:
- Select fruits and/or vegetables to your taste (apples, melon, pear, etc.)
- Cut the plant flower directly from the pot
- Shake all ingredients and drink the juice as soon as possible
In this video we explain step by step how to make fresh cannabis juice ... Press play!
1. Izzo, A et al. (2009) Non-psychotropic plant cannabinoids: new therapeutic opportunities from an ancient herb. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 730, 1-13
2. Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ (2001). "The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology". Cell 104 (4): 487–501
3. Malfait AM, Gallily R, Sumariwalla PF et al. The non-psychoactive cannabis-constituent cannabidiol is an oral anti-arthritic therapeutic in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000;97:9561–6.
4. Blake DL. et al. (2006) Preliminary assessment of the efficacy, tolerability and safety of a cannabis-based medicine (Sativex) in the treatment of pain caused by rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 45:50-52
5. Parker, L.A. et al. (2006) Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol, but not ondansetron, interfere with conditioned retching reactions elicited by a lithium-paired context in Suncus murinus: An animal model of anticipatory nausea and vomiting.Physiol. Behav. 87, 66–71
6. Ma, Y.L. et al. (2008) The phytocannabinoid Delta(9)-tetrahydrocannabivarin modulates inhibitory neurotransmission in the cerebellum. Br. J. Pharmacol. 154, 204–215
7. Zuardi, A.W. (2008) Cannabidiol: from an inactive cannabinoid to a drug with wide spectrum of action. Rev. Bras. Psiquiatr. 30, 271–280
8. Resstel, L.B. et al. (2009) 5-HT1A receptors are involved in the cannabidiol-induced attenuation of behavioural and cardiovascular responses to acute restraint stress in rats. Br. J.Pharmacol. 156,181–188
9. Scutt, A. and Williamson, E.M. (2007) Cannabinoids stimulate fibroblastic colony formation by bone marrow cells indirectly via CB2 receptors. Calcif. Tissue Int. 80, 50–59
10. Mechoulam, R. et al. (2007) Cannabidiol recent advances. Chem.Biodivers. 4, 1678–1692
11. Krenzler, B. (2013) A look into raw, organic, cannabis juicing. CannaDad's Blog.
12. Esposito, G. et al. (2006) The marijuana component cannabidiol inhibits beta-amyloid-induced tau protein hyperphosphorylation through Wnt/beta-catenin pathway rescue in PC12 cells. J. Mol.Med. 84, 253–258



Comments from our readers
There are no comments yet. Would you like to be the first?
Leave a comment!Did you like this post?
Your opinion about our seeds is very important to us and can help other users a lot (your email address won't be made public).