- Humidity and other environmental factors can bring about the appearance of fungi on your cannabis plant, an unpleasant visit that can appear without warning.
- Fungi are silent fellow travellers that settle on your plants, and they are a powerful danger for your crop.
- Much like in the film Alien, they wait patiently hiding in the dark, thousands of dormant spores waiting for the conditions to be right (heat, humidity, poor ventilation) so that they can start their star appearance.
- If you are not attentive and you take your time in detecting them, the consequences could be fatal, as although there are numerous remedies to combat and prevent them, when they completely take over the plant, they are very capable of spoiling every effort you have put into them for months.

The first step to take in preventing the appearance of any type of fungus is prevention, so before explaining which the most common fungi are, here are a few tips:
- Hygiene is a fundamental factor when it comes to the appearance of fungi. If you are growing plants indoors, between each crop we recommend that you completely disinfect the area, both in the wardrobe and anything that could have come into contact with the plants (utensils, plant pots). You can do this by using fungicides or simply using 5% bleach solution. For the duration of the crop, keep the area tidy and clean and, if you want to take further measures, you can also change your clothes when entering the room where you have your crops, as they may contain spores and infect the area. For plants grown outdoors it is more difficult to control this, but you can establish a cleaning system for all of the utensils that you use.
- Clean the remains of vegetables, dead leaves and the waste from decomposition, which are all perfect for some fungi.
- Control the temperature and humidity: for fungi to be able to grow, they need certain environmental conditions, which are basically heat, humidity and poor ventilation. If you pay attention to ensure that your crop is suitably ventilated, that relative humidity does not exceed 50% in the flowering phase and that the temperature does not exceed 25 ºC, then you've already won half the battle. It is true that when plants are outside these elements don't depend on you, therefore try not to let your crop run too late, because in October the necessary climatic conditions (rain, humidity) appear so that these undesirable diners can move in.
- Use preventive measures: they don't have to be chemical ones, there are numerous organic products with an effective fungicide action. You can buy them at your local grow shop or make them yourself.
- If you use cuttings that come from outside your home, check that the mother plant that they come from is healthy, there is no point in performing a thorough cleaning of your space if later you find that you have planted infected cuttings.
However, if you follow this advice thoroughly then the chances of fungi appearing will be considerably reduced, but there is no method that is 100% effective. Spores are microscopic bodies designed to survive over long periods of time in extreme conditions, they travel in the air, and you may have the bad luck that their final destination is your crop. Detecting the symptoms and signs of infection in time can be crucial for your crop, below we describe some of the most common fungi that may affect cannabis, how to identify them and their treatment.
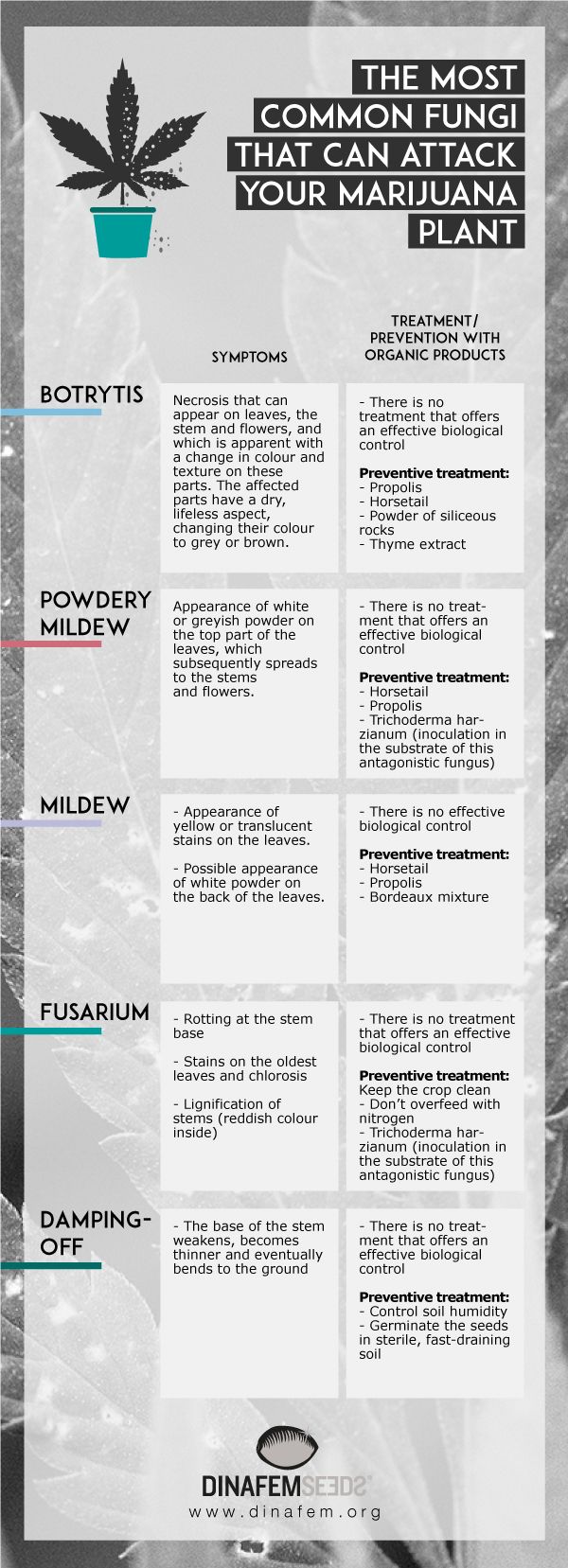
Botrytis
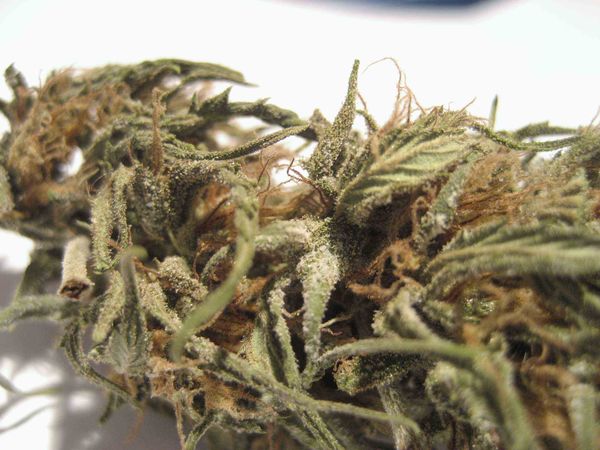 How to recognise this fungus
How to recognise this fungus
Botrytis or grey mould is a pathogenic fungus and it is one of the most common fungi to be found on marijuana plants. The good news is that this fungus is very difficult to detect, you will understand this if you ever come across it, as it is a necrosis process that can affect any part of the plant (roots, stems, leaves, buds), and this is visibly reflected by the colour and texture of them, which will turn from brown to grey, with a dry, lifeless aspect. The bad news is that it spreads fast and it is capable of killing off your plant in a matter of days. That is why you need to act in a fast and effective manner.
What to do if your plants have been infected with botrytis
Humidity is the main factor for the appearance of this fungus, therefore, if you can avoid it, follow our advice as indicated above and keep humidity levels controlled at all times. Nevertheless, if the fungus has already infected the plant, the first thing you need to do is to cut off the infected parts, also taking off a few centimetres of the healthy part, in order to leave a safety margin. Don't let the infected buds contaminate other parts of the plant or the healthy buds, and once you have cut them off, destroy them and clean the scissors used and your hands well. After cutting, ventilate the room well in order to reduce the level of humidity, increase the temperature to 26 ºC and reduce the humidity to less than 50%. Botrytis normally appears at the end of the flowering period, so if this is your case, our advice is that you harvest as soon as possible, only that way will you stop the infection. Cutting off the infected parts does not guarantee at all that you have got rid of the fungus.
Although there are chemical products available to spray on marijuana plants as a preventive measure, we don't recommend that you use them for various reasons: to start with, spraying is not a 100% guarantee that this fungus will not appear later on and, what is more important, these products leave a film of chemicals that can be harmful for the health, remember that everything that you use on yourmarijuana plants will go into your body when you consume it. Therefore, what we recommend to be most effective is to avoid the conditions for the appearance of the fungus, always controlling the humidity, maintaining hygiene and controlling the density of your crop. Our advice is that you take the aforementioned measures and perhaps experiment with some ecological anti-fungus products, like for example propolis or horsetail, for preventive purposes.
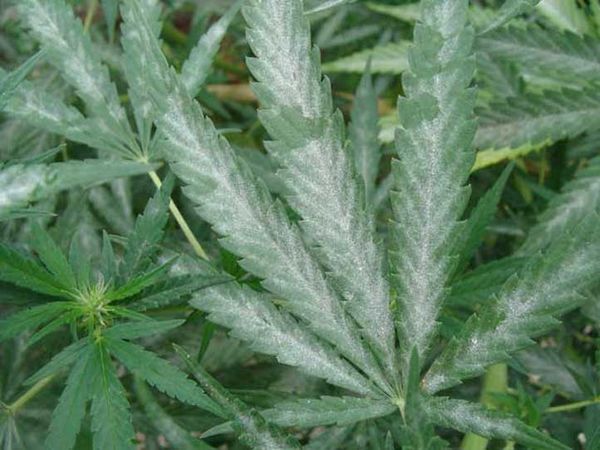
Powdery mildew
This fungus is one of the most common to affect marijuana plants, it needs high humidity and a minimum temperature of 20ºC to be able to grow and sudden changes in temperature benefit its appearance. Although an infection of powdery mildew is easy to identify, and it does have a treatment, if a remedy is not used in time, the consequences can be fatal.
How to identify powdery mildew
It will be easy for you to realise that your crop is infected with powdery mildew, as this fungus covers the leaves and buds, on which a layer of white dust appears, generally located on the top part. In an initial phase, you will be able to see small circles of white dust on the leaves which, as the infection progresses, will spread and intensify in density, until the stem and buds are also affected.
Treatment
Despite it not being one of the most lethal fungi, it is worthwhile getting rid of it in time, as once it has entered the bud, it is very difficult to get rid of and the flowers that are infected with this fungus will not be in any way suitable for consumption. In order to prevent the appearance of this fungus, you can use horsetail or propolis or some organic fungicides, this way you will avoid your plants from being sprayed or watered with chemical products. Various studies have demonstrated that the inoculation of the antagonistic fungus called Trichoderma harzianum (an antagonistic fungus of pathogenic fungi), used in the soil for the planting, effectively prevents the appearance of powdery mildew.
Mildew (Phytophthora infestans)
Mildew is a fungus that has symptoms that are very similar to those of powdery mildew, however there are some differences between them that can help you to tell them apart.
How to know if your plant has mildew
This fungus, which affects the leaves, stems and flowers, does not only appear on the top of the plant, but unlike powdery mildew, it is normally found on the underside of the leaves. The first symptoms that indicate a mildew infection are the appearance of small yellow or translucent stains on the leaves that are shortly followed (not always) by a fine layer of white dust located on the back of the leaves.
Treatment
The first thing that you should do if you find out that your crop is infected is to improve its ventilation, prune the affected areas and avoid overcrowding, so ensure that there is enough space between plants. Then you should apply a fungicide to eliminate the fungus. There are various products that can help you to eliminate this fungus, some are contact products and they are applied after the first 24 hours of infection, and others are systemic that are used after a maximum of 72 hours from the appearance of the fungus. Just like in the previous cases, we don't recommend the use of chemical products to treat mildew, because of its health risks, a good organic preventive remedy for this fungus is Bordeaux mixture.
Fusarium
The term Fusarium covers a wide range of filamentous fungi that live in the soil. These fungi are parasites that feed on the plant, making it sick and eventually killing it.
How to identify Fusarium
Fusarium blocks the sap flow within the plant, which causes rotting at the stem base, stains on the oldest leaves and chlorosis. At times, the tip of the leaves curl upwards and eventually wilt. Another typical symptom of Fusarium is the lignification of stems. If you cut one in two and look inside, you will see they are reddish brown.
Treatment
Sadly, there is no effective treatment against Fusarium yet. Thus, the best you can do is dispose of infested plants and try to save the ones that look healthy.
Damping off
This disease is caused by a variety of fungi and affects young seedlings when grown in non-sterile soil, which tends to be highly humid and lack ventilation.
How to identify damping-off
Damping off usually attacks the section of the plant that is closer to the soil, namely the base of the stem, which weakens, becomes thinner and eventually bends to the ground. This process is very fast and can happen overnight.
Treatment
As we have just pointed out, damping off moves very fast, so there's little you can do about it once it hits the plants. Anyway, it is a good idea to dispose of the infested seedlings promptly to stop its propagation. As a preventive measure, you can use Pythium oligandrum – a parasite that feeds on fungi – always in sterile soil.
Alternaria
Alternaria is a fungus that belongs to the family of Pleosporaceae, which includes 44 different species. It grows during the decomposition of organic matter, meaning that it can be found all around the world.
How to recognise Alternaria
Alternaria produces dry, round, grey to black spots that tend to affect the leaves and the stem. These come become necrotic and weaken the plant significantly, leading to poor nutrient absorption that results in a number of visually perceptible deficiencies.
Treatment
The best way to eliminate this fungus is keeping the crop clean (with particular attention to plant remains), ensuring uniform ventilation (avoid humidity pockets), providing the right amount of water and using preventive treatments (broad-spectrum fungicides).





Comments from our readers
Read comments in other languages:
Did you like this post?
Your opinion about our seeds is very important to us and can help other users a lot (your email address won't be made public).